Definition: The gradual loss of backlinks over time due to content removal, site restructuring, domain expiration, or editorial changes. Link decay directly impacts Domain Rating (DR), PageRank flow, link graph integrity, and organic rankings by reducing the total link equity flowing to your site and degrading crawl efficiency.
📉 Average Annual Loss 8-15% of Links
⚠️ Primary Cause Content Removal
🔍 Detection Method Backlink Monitoring
🛡️ Prevention Proactive Monitoring
📊 Link Decay Impact by Cause
| Cause | Frequency | Recoverability | SEO Impact |
| 🗑️ Content deletion | 35% of decay | Low | High — permanent equity loss |
| 🔄 URL restructuring | 25% of decay | High | Medium — recoverable via redirects |
| 💀 Domain expiration | 15% of decay | Very Low | Very High — total link loss |
| ✏️ Editorial removal | 15% of decay | Medium | Medium — relationship recovery |
| 🚫 Nofollow conversion | 10% of decay | Low | Medium — equity stops flowing |
In 2026, link decay represents one of the most overlooked threats to SEO performance. While most SEO strategies focus on acquiring new backlinks, few account for the natural erosion of existing links. Studies show that websites lose 8-15% of their backlink profile annually through various decay mechanisms.
🎯 The Hidden Cost of Link Decay
Link decay creates a compounding negative effect on your authority:
- Immediate Loss — Direct reduction in referring domains and link equity
- Ranking Degradation — Decreased authority for competitive keywords
- Competitor Advantage — Your decay becomes their relative gain
- Acquisition Waste — New links offset losses instead of building net authority
Without monitoring, you may be running to stand still—acquiring links just to replace decayed ones.
TL;DR: Link Decay Quick Reference
- Link decay = Natural loss of backlinks over time (8-15% annually)
- Primary causes = Content deletion, URL changes, domain expiration, editorial removal
- Detection = Regular backlink monitoring and comparison snapshots
- Prevention = High-quality link building, relationship nurturing, monitoring alerts
- Recovery = Reclamation outreach, redirect requests, content archiving
- For automated link decay monitoring: Link Laboratory
- For competitor decay analysis: SearchAtlas
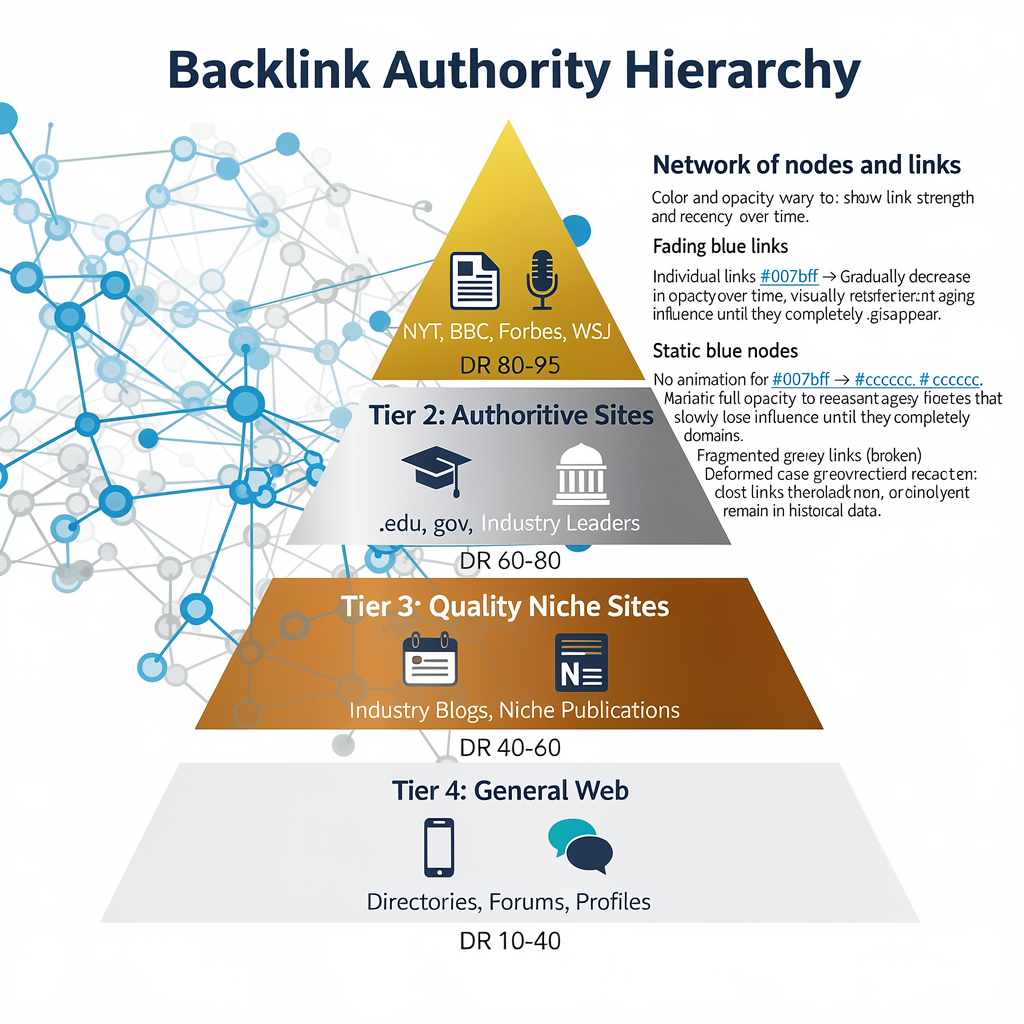
What Is Link Decay
Link decay (also called “link rot” or “link attrition”) refers to the gradual disappearance or devaluation of backlinks pointing to your website over time. Unlike sudden algorithmic penalties, link decay happens gradually and often goes unnoticed until significant authority loss occurs.
⏳ Evolution of Link Decay Awareness
- 2010
Early Link Building Era: Focus entirely on acquisition. Link maintenance considered unnecessary. - 2015
Link Quality Focus: Penguin updates shift attention to link quality, but decay still overlooked. - 2020
Backlink Monitoring Emergence: Tools begin tracking link losses. Industry recognizes decay as ranking factor. - 2026
Proactive Link Health: Link decay monitoring becomes standard practice. AI-powered prediction of at-risk links.
The Link Decay Lifecycle
Link Lifecycle Stages
- 01
Acquisition Phase
New backlink is created through Outreach, Content Marketing, or Natural Discovery.
Status: Active, full equity transfer - 02
Stable Phase
Link remains active and passes Link Equity consistently. Typical duration: 6 months to several years.
Status: Healthy, monitoring recommended - 03
At-Risk Phase
Warning signs appear: Page Updates, Site Restructuring, Declining Site Health.
Status: Intervention opportunity - 04
Decay Phase
Link becomes Broken (404), Redirected, Nofollowed, or Removed.
Status: Recovery action required
Link Decay vs Link Devaluation
| Aspect | Link Decay | Link Devaluation |
| Definition | Physical loss or removal of backlinks | Algorithmic reduction in link value |
| Cause | External factors (site changes, deletions) | Google algorithm updates |
| Detection | Backlink monitoring tools | Ranking/traffic analysis |
| Recoverability | Often recoverable through outreach | Requires link profile improvement |
| Timeline | Gradual and ongoing | Sudden (post-update) |
Link Equity Domain Authority Referring Domains Link Reclamation 404 Errors 301 Redirects
Causes of Link Decay
Understanding why links decay helps you predict and prevent losses before they impact your rankings.
Primary Causes of Link Decay
🔗 Link Decay Causes by Frequency
🗑️ #1: Content Deletion (35% of decay)
Description: Linking page or entire site is removed from the web Recoverability: Very Low Prevention: Target evergreen, authoritative sources
🔄 #2: URL Restructuring (25% of decay)
Description: Site migration, CMS change, or URL cleanup without proper redirects Recoverability: High (if caught early) Prevention: Monitor linking site health, request redirect preservation
💀 #3: Domain Expiration (15% of decay)
Description: Linking domain expires and goes offline or is acquired by new owner Recoverability: Very Low Prevention: Diversify link sources, monitor domain health
✏️ #4: Editorial Removal (15% of decay)
Description: Content is updated and your link is removed or replaced Recoverability: Medium (relationship-dependent) Prevention: Provide exceptional value, maintain relationships
🚫 #5: Nofollow Conversion (10% of decay)
Description: Dofollow link is changed to nofollow, stopping equity transfer Recoverability: Low Prevention: Build genuine editorial relationships
Decay Triggers by Source Type
| Source Type | Decay Risk | Common Triggers |
| Blog Posts | 🔴 High | Content pruning, site pivots, author departure, CMS migrations |
| News Articles | 🟡 Medium | Archive policies, paywall implementation, site restructuring |
| Resource Pages | 🟢 Low-Medium | Link audits, broken link removal, resource updates |
| Educational (.edu) | ⚪ Low | Course updates, faculty changes, site migrations (rare) |
⚠️ High-Risk Link Types
Some link sources have inherently higher decay rates:
- Guest posts on small blogs — Sites frequently shut down or pivot
- Startup/company pages — High business failure rate
- Forum signatures — Profile deletions, forum closures
- Press releases — Often removed after expiration period
- Sponsored content — May be removed when contract ends
Diversify your link profile to reduce concentration risk.
The SEO Impact of Link Decay
Quantifying Link Decay Impact
⚖️ Link Decay Risk Assessment
The SEO impact of link decay depends on the quality and quantity of lost links relative to your total profile.
📉 Authority Erosion
Each lost referring domain reduces your Domain Rating. High-DR losses have disproportionate impact.
Formula: DR impact ≈ Lost Link DR × (1 / Total RDs)
🎯 Ranking Volatility
Pages with fewer supporting links experience greater ranking fluctuations when links decay.
Threshold: Pages with <10 linking domains are most vulnerable
💸 Acquisition ROI Reduction
Link building investment is wasted if decay rate exceeds acquisition rate. Net authority becomes negative.
Target: Maintain acquisition rate ≥ 2× decay rate
🤖 Crawl Budget Waste
404 errors from decayed links consume crawl budget as Googlebot repeatedly attempts to follow dead paths, reducing crawl depth for valuable pages.
Connection: Link decay directly impacts Technical SEO through crawl efficiency
Link Decay Impact Model
🧩 Link Decay Cause-Effect Relationships
| Cause (Input) | Relationship | Effect (Output) |
| Link Decay | reduces | Referring Domain Count |
| Referring Domain Loss | decreases | Domain Rating (DR) |
| DR Decline | weakens | Ranking Competitiveness |
| Ranking Loss | reduces | Organic Traffic & Revenue |
| 404 Errors (Decay) | wastes | Crawl Budget |
| Crawl Budget Waste | reduces | Crawl Depth & Index Coverage |
Industry Benchmarks: Acceptable Decay Rates
| Industry | Average Annual Decay | Acceptable Threshold | Action Trigger |
| SaaS/Tech | 12-18% | <15% | >15% |
| E-commerce | 10-15% | <12% | >12% |
| Publishing | 8-12% | <10% | >10% |
| Finance | 6-10% | <8% | >8% |
| Healthcare | 5-8% | <7% | >7% |
💡 The Decay Treadmill Effect
Consider this scenario:
- You have 500 referring domains
- Annual decay rate: 12% (60 lost links/year)
- To maintain authority: Acquire 60+ new links/year just to stay even
- To grow authority: Need 120+ new links/year (2× decay rate)
Without tracking decay, you might celebrate 80 new links while unknowingly losing 60—net gain of only 20.
The Crawl Efficiency Bridge: Connecting Link Decay to Technical SEO
Link decay isn’t just an Off-Page SEO concern—it directly impacts Technical SEO through crawl efficiency degradation.
🔗↔️🤖 How Link Decay Affects Crawl Budget
| Decay Event | Technical Impact | Crawl Consequence |
| 404 Error (Link Points to Deleted Page) | Googlebot follows dead path | Crawl budget wasted on non-existent resource |
| Redirect Chain (3+ hops) | Multiple requests per link | Reduced crawl depth for valuable pages |
| Soft 404 (Empty/Thin Page) | Bot indexes low-value content | Dilutes crawl priority signals |
| Domain Expiration | External 404 or parked page | Googlebot may reduce crawl frequency to your site |
🤖 The PageRank-Crawl Connection
Google’s original PageRank algorithm used the link graph to determine crawl priority. When links decay:
- Reduced Link Signals → Lower perceived importance → Reduced crawl frequency
- Broken Inbound Links → Wasted crawler resources → Less budget for deep pages
- Link Graph Fragmentation → Orphaned pages → Indexation gaps
Maintaining link graph integrity through the Link Preservation Protocol (LPP) directly supports crawl efficiency.
Detecting Link Decay
Link Health Monitoring Framework
🧪
Recommended Tool: Link Laboratory
Automated link decay detection with real-time alerts, historical tracking, and recovery recommendations.
Detection Methods
Method 1 Automated Monitoring (Recommended)
- Set up continuous backlink crawling with tools like Link Laboratory
- Configure alerts for lost links, broken links, and status changes
- Track referring domain count trends over time
- Monitor competitor decay rates for benchmarking
Method 2 Periodic Snapshot Comparison
- Export backlink profile monthly from your monitoring tool
- Compare current snapshot to previous period
- Identify newly lost referring domains
- Categorize losses by cause (404, redirect, nofollow, etc.)
Method 3 Manual Spot Checks
- Regularly verify high-value backlinks still exist
- Check link status (dofollow, anchor text, placement)
- Confirm linking page still ranks and receives traffic
- Validate redirect chains haven’t broken equity flow
Key Decay Indicators
🚨 Critical Indicators (Immediate Action)
- Referring domain count dropping month-over-month
- High-DR links returning 404 errors
- Multiple links from same domain suddenly lost
- Domain Rating declining without explanation
⚠️ Warning Indicators (Monitor Closely)
- Linking pages showing reduced organic traffic
- Linking sites undergoing redesign or migration
- Dofollow links converted to nofollow
- Anchor text or link placement changed
📊 Trend Indicators (Strategic Review)
- Decay rate exceeding industry benchmarks
- Specific link types decaying faster than others
- Competitor gaining while you’re losing links
- Seasonal patterns in link losses
Link Decay Prevention Strategies
The Link Preservation Protocol (LPP)
The Link Preservation Protocol (LPP) is a systematic four-pillar framework for minimizing link decay and maintaining link graph integrity over time.
LPP Pillar 1 Build Decay-Resistant Links
- ✅ Target authoritative, established sites with long track records
- ✅ Prioritize editorial links over transactional placements
- ✅ Diversify across industries, geographies, and site types
- ✅ Avoid link sources with high historical decay rates
LPP Pillar 2 Create Link-Worthy Assets
- ✅ Develop evergreen resources that remain valuable over time
- ✅ Build tools, calculators, and interactive content
- ✅ Maintain and update linked content regularly
- ✅ Ensure your content continues to deserve the link
LPP Pillar 3 Nurture Relationships
- ✅ Maintain contact with key linking site owners/editors
- ✅ Provide ongoing value beyond the initial link request
- ✅ Offer to update your content if their needs change
- ✅ Be a resource, not just a link requester
LPP Pillar 4 Implement Monitoring
- ✅ Set up automated backlink monitoring with [Link Laboratory](https://linklaboratory.com)
- ✅ Configure alerts for lost links and status changes
- ✅ Schedule monthly decay reports and analysis
- ✅ Track decay rates by link source category
Link Quality Scoring for Decay Resistance
| Factor | High Decay Risk | Low Decay Risk |
| Site Age | <2 years | >5 years |
| Content Type | News, trending topics | Evergreen resources |
| Site Authority | DR <40 | DR >60 |
| Business Model | Startup, affiliate | Enterprise, education |
| Link Placement | Footer, sidebar | In-content, contextual |
| Editorial Process | Self-published | Edited, reviewed |
Link Recovery Tactics
Link Reclamation Workflow
👥 Recovery Team Roles
The Monitor
Tracks Link Status Changes and triggers Recovery Alerts.
The Analyst
Assesses Recovery Priority based on Link Value and Recoverability.
The Outreach Specialist
Executes Recovery Communications and Relationship Rebuilding.
The Content Manager
Updates Linked Assets and creates Replacement Content if needed.
Recovery Tactics by Decay Type
| Decay Type | Detection Signal | Recovery Tactic | Success Rate |
| 404 – Page Deleted | Link returns 404 status | Contact site owner, suggest redirect or new placement | 15-25% |
| 301 – Redirected Away | Link redirects to different page | Request redirect update to preserve link | 30-40% |
| Editorial Removal | Page exists but link removed | Outreach to editor, offer updated resource | 20-35% |
| Nofollow Conversion | Link changed to nofollow | Discuss value proposition, request reconsideration | 10-20% |
| Domain Expiration | Domain no longer resolves | Monitor for new ownership, reach out if reactivated | 5-10% |
Recovery Outreach Templates
📧 404 Recovery Template Copy and customize
Subject: Quick fix for broken link on [Page Title]
Hi [Name],
I noticed that a page on [Site Name] that previously linked to our [Resource Name] is now returning a 404 error:
Original URL: [URL]
If you’re restructuring or updating content, I wanted to offer an updated version of our resource that might be helpful: [New URL]
If there’s a new location for this content, I’d be grateful if you could consider including the link there.
Thanks for your time,
[Name]
📧 Editorial Removal Recovery Template Copy and customize
Subject: Updated resource for [Article Topic]
Hi [Name],
I noticed our [Resource Name] was previously referenced in your excellent article on [Topic]. I understand content evolves over time!
Since then, we’ve significantly updated our resource with:
- [New data/feature 1]
- [New data/feature 2]
- [New data/feature 3]
If this updated version would be valuable to your readers, I’d be honored to be included again: [URL]
Best regards,
[Name]
Building Decay-Resistant Links
Link Source Quality Matrix
| Source Category | Decay Rate | Best Use Case | Acquisition Difficulty |
| Academic (.edu) | 2-5%/year | Research citations, resources | High |
| Government (.gov) | 1-3%/year | Official resources, data | Very High |
| Major Publications | 5-8%/year | News coverage, thought leadership | High |
| Industry Resources | 8-12%/year | Niche authority, topic relevance | Medium |
| Corporate Sites | 10-15%/year | Partnerships, mentions | Medium |
| Blog Networks | 15-25%/year | Volume, diversity | Low |
💡 The 80/20 Rule for Link Decay
Focus your link building investment strategically:
- 80% of effort → Decay-resistant sources (major publications, .edu, .gov, established industry sites)
- 20% of effort → Higher-decay but easier sources (blogs, niche sites, newer publications)
This creates a stable foundation while maintaining link velocity.
Evergreen Link Assets
Build content that naturally attracts and retains links over time:
🏗️ Decay-Resistant Asset Types
High-Retention Assets
- ✅ Original Research & Data — Studies others cite
- ✅ Comprehensive Guides — Definitive resources on topics
- ✅ Tools & Calculators — Utility that provides ongoing value
- ✅ Industry Glossaries — Reference material people bookmark
High-Decay Assets (Avoid Over-Reliance)
- ⚠️ Trend-based Content — Becomes outdated quickly
- ⚠️ News Commentary — Short relevance window
- ⚠️ Product Reviews — Products change/discontinue
- ⚠️ Event Coverage — Time-bound interest
Link Decay Monitoring Setup
Monitoring Stack Recommendations
🧪
Primary: Link Laboratory
Real-time link monitoring, decay alerts, historical tracking, and automated recovery recommendations.
📊
Supplementary: SearchAtlas
Competitor decay analysis, link opportunity identification, and comprehensive SEO intelligence.
Alert Configuration Best Practices
🔔 Recommended Alert Thresholds
| Alert Type | Threshold | Response Time |
| High-DR Link Lost | Any DR 60+ link | 24-48 hours |
| Bulk Link Loss | >5 links from same domain | Immediate |
| Weekly Decay Rate | >2% of total links | Weekly review |
| Monthly Decay Rate | >5% of total links | Monthly audit |
| Competitor Gain | Competitor gains lost link | 48-72 hours |
Monthly Decay Report Template
| Metric | This Month | Last Month | Trend | Action |
| Total Referring Domains | [X] | [Y] | [↑/↓] | [Continue/Investigate] |
| Links Lost | [X] | [Y] | [↑/↓] | [Review causes] |
| Links Gained | [X] | [Y] | [↑/↓] | [Assess net position] |
| Net Change | [X] | [Y] | [↑/↓] | [Adjust strategy] |
| Decay Rate | [X%] | [Y%] | [↑/↓] | [Compare to benchmark] |
| Recovery Success | [X/Y] | [X/Y] | [↑/↓] | [Refine outreach] |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is link decay?
Link decay is the gradual loss of backlinks over time due to content deletion, URL changes, domain expiration, or editorial removal. The average website loses 8-15% of its backlinks annually through natural decay, directly impacting PageRank flow, domain authority, and rankings.
How fast do backlinks decay?
Backlinks decay at an average rate of 8-15% per year, but rates vary significantly by source type. Blog links decay fastest at 15-25% annually, while educational (.edu) links decay at only 2-5% per year. High-authority, established sites consistently show the lowest decay rates.
Can I recover lost backlinks?
Yes, you can recover many lost backlinks through targeted outreach and the Link Preservation Protocol. Recovery success rates vary by decay type: 30-40% for redirect issues, 20-35% for editorial removals, and 15-25% for 404 errors. The key is detecting decay quickly and reaching out while the opportunity exists.
How do I monitor link decay?
You monitor link decay using automated backlink monitoring tools like Link Laboratory that track your link profile continuously. Set up alerts for lost links, status changes, and decay rate thresholds. Compare monthly snapshots to identify trends and prioritize recovery efforts.
What causes backlinks to disappear?
Backlinks disappear due to five primary causes: content deletion (35%), URL restructuring without redirects (25%), domain expiration (15%), editorial removal (15%), and conversion to nofollow (10%). Understanding the specific cause helps determine the appropriate recovery approach.
How does link decay affect SEO?
Link decay affects SEO by reducing your referring domain count, which directly impacts PageRank flow, Domain Rating, and ranking competitiveness. Additionally, 404 errors from decayed links waste crawl budget as Googlebot follows dead paths. Each lost high-DR link has disproportionate impact, and if decay rate exceeds acquisition rate, your link graph integrity declines even while actively building links.
Which links are most resistant to decay?
The most decay-resistant links come from established institutions (.edu, .gov), major publications, and sites with long track records—these have the lowest decay rates (2-8% annually). Editorial links to evergreen content in high-authority contexts are most stable. Following LPP Pillar 1, avoid over-reliance on blog networks, startups, and trend-based content.
How often should I check for link decay?
You should check for link decay continuously using automated monitoring tools, with formal decay audits monthly. Set immediate alerts for high-value link losses (DR 60+) and weekly alerts for unusual decay patterns. Quarterly strategic reviews should assess decay trends against industry benchmarks as outlined in LPP Pillar 4.
Link Decay Glossary
🧩 Key Link Decay Relationships
| Subject (Entity) | Predicate (Relationship) | Object (Entity/Concept) |
| Link Decay | reduces | Domain Authority |
| Backlink Monitoring | detects | Link Decay |
| Link Reclamation | recovers | Decayed Links |
| Evergreen Content | prevents | Editorial Link Removal |
| Link Preservation Protocol | maintains | Link Graph Integrity |
| 404 Errors | waste | Crawl Budget |
Link Decay
The gradual loss of backlinks over time through various mechanisms including deletion, restructuring, and editorial changes. Also known as “link rot” or “reference rot” (see: Wikipedia: Link Rot).
Link Rot
Another term for link decay, emphasizing the organic degradation of link profiles over time.
Decay Rate
The percentage of backlinks lost over a specific period, typically measured annually.
Link Reclamation
The process of recovering lost or broken backlinks through outreach and relationship management.
Referring Domain
A unique domain that links to your website. Decay is often measured by referring domain losses. In link analysis, one referring domain may contain multiple backlinks (pages linking to you).
Link Attrition
The natural reduction in link count over time, similar to customer attrition in business contexts.
Backlink Monitoring
Systematic tracking of your backlink profile to detect changes, losses, and opportunities.
Decay-Resistant Links
Backlinks from stable, authoritative sources with historically low decay rates.
Link Velocity
The rate of link acquisition or loss over time. Positive velocity indicates net growth.
404 Error
HTTP status code indicating a page no longer exists, a common cause of link decay and crawl budget waste (see: Wikipedia: HTTP 404).
Link Preservation Protocol (LPP)
A systematic four-pillar framework for minimizing link decay: (1) Build decay-resistant links, (2) Create link-worthy assets, (3) Nurture relationships, (4) Implement monitoring.
PageRank
Google’s foundational algorithm for measuring page importance based on the quality and quantity of incoming links. Link decay directly reduces PageRank flow (see: Wikipedia: PageRank). Often referred to as “link equity” or “link juice” in SEO contexts.
Link Graph Integrity
The structural health of your backlink network, including the consistency and validity of link connections over time.
Crawl Budget
The number of pages Googlebot will crawl on your site within a given timeframe. 404 errors from decayed links waste crawl budget by directing bots to non-existent pages (see: Google: Crawl Budget).
Crawl Depth
How many clicks from the homepage Googlebot travels to discover pages. Wasted crawl budget from decay reduces effective crawl depth.
301 Redirect
A permanent redirect that passes approximately 90-99% of link equity from the old URL to the new URL. Essential for recovering decayed links when URLs change (see: Wikipedia: HTTP 301).
Link Graph
The interconnected network of hyperlinks across the web that search engines use to discover, crawl, and rank pages. Link decay fragments this graph, reducing discoverability.
Key Takeaways: Managing Link Decay in 2026
- Link decay is inevitable — Expect 8-15% annual loss; plan acquisition accordingly
- Implement the Link Preservation Protocol (LPP) — Follow all four pillars systematically
- Monitor continuously — Use Link Laboratory for automated decay detection
- Prioritize recovery — High-DR links warrant immediate outreach when lost
- Protect link graph integrity — Target authoritative, established sources (LPP Pillar 1)
- Prevent crawl budget waste — 404s from decay hurt Technical SEO; clean up dead links
- Maintain PageRank flow — Ongoing relationships prevent editorial removal (LPP Pillar 3)
- Benchmark your rate — Compare decay to industry standards and competitors
- Acquisition must exceed decay — Target 2× decay rate for meaningful authority growth
Ready to protect your backlink investment?



